Agroprocessing

Agribusiness in Tonga: A Strategic Pillar for Growth and Trade
- Backbone of the economy and trade: Agriculture contributes approximately 19% of Tonga’s GDP and supports livelihoods, food security, and rural employment across the islands. Over the past three years, it has also accounted for around 70% of total exports, making it a cornerstone of Tonga’s trade and foreign exchange earnings.
- Policy-backed transformation: Agribusiness development is guided by the Tonga Agriculture Sector Plan (2016–2020) and the Tonga Strategic Development Framework (TSDF), with support from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forests and Food (MAFFF) Corporate Plan and the Joint National Action Plan for Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Management (JNAP).
- From subsistence to scale: While agriculture remains largely small-scale and subsistence-based, momentum is building toward commercial farming and agribusiness, supported by both public and private sector initiatives.
Export-oriented priority crops with investment potential
Investment opportunities
1. Agro-processing & value addition
- Root crop: Processing of cassava, taro and yams into flour, frozen goods, chips, or dried products.
- Coconut-based products: Manufacturing of virgin coconut oil (VCO), cream, coir fiber, and artisanal by-products.
- Tropical fruit: Processing (e.g., pineapple, watermelon, papaya) into juices, dried snacks, and preserves.
- Vanilla: Curing, grading, and packaging.
2. Supply chain & export infrastructure
- Post-harvest logistics: Cold storage, warehouses, grading and packing facilities, and refrigerated transport.
- Certification & compliance: Services for organic certification, traceability, and export-standard verification.
3. Livestock & animal feed
- Livestock production and processing: Poultry and piggery farms, along with slaughterhouses and meat processing facilities, to reduce reliance on imports.
- Feed manufacturing: Development of feed mills using local crop by-products.
4. Input supply, and support services
- Agri-input distribution: Supply of seeds, fertilizers, tools, and irrigation systems.
- Agri-finance solutions: Microcredit, leasing, and tailored financing models for smallholders and cooperatives
- Technical training & advisory services: Centers or mobile services to deliver Good Agricultural Practices (GAP), export compliance, and productivity training.
- Digital agribusiness platforms: Mobile and e-commerce solutions connecting farmers to markets, streamline logistics and payments, and improve access to training and financing.

Agricultural Sector Insights
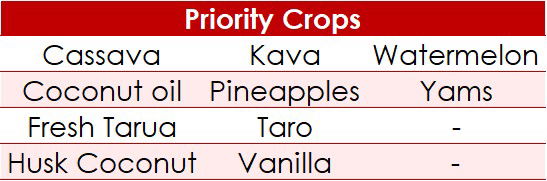
- Land availability and relevance: Tonga has approximately 350 km² of agricultural land, ranking mid-range among Pacific Island nations.
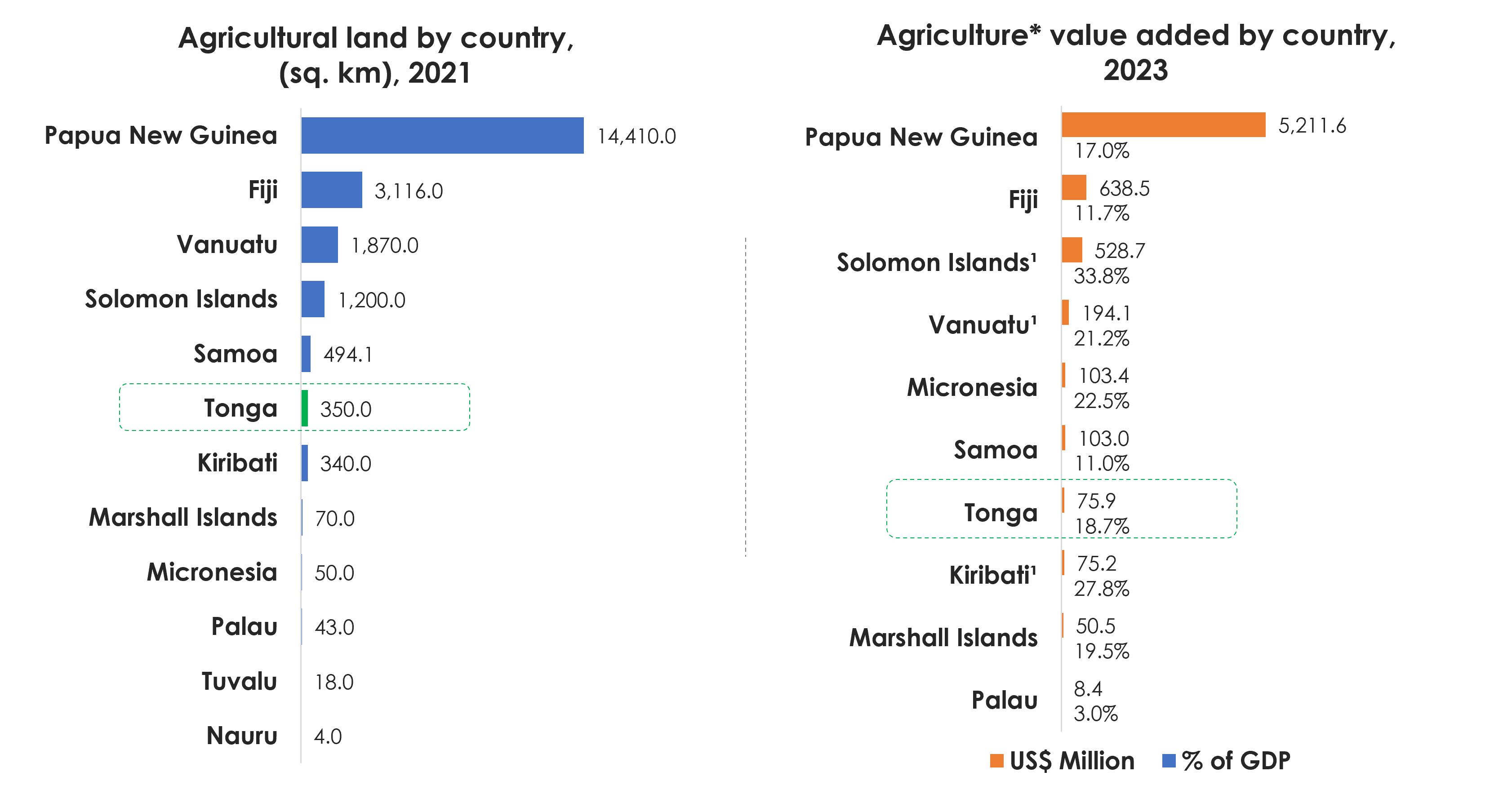
- Consistent economic contribution: Agriculture, forestry, and fisheries contributed US$75.9 million to Tonga’s economy in 2023, representing 18.7% of GDP. The sector plays a central role in livelihoods, food security, and rural employment.
* Agriculture, forestry, and fishing (current process). - ¹ Values for 2022. - Source: World Bank
- Rising contribution to GDP: While absolute values have fluctuated, the agriculture sector’s share of GDP rose to its highest point since 2019, indicating resilience and growth potential.
- Key crop contributors: Yams led all agricultural products with a value of US$61.7 million (39.7%), followed by coconuts at US$38.2 m (24.6%), and lemons and limes with US$16.3m (10.5%). Combined these 3 products represent over 75% of the sectoral gross production value.
- Harvested area: Pumpkins, squash, and gourds lead with 2,292 hectares (11.8% of total), followed by coconuts (2,117 ha, 10.9%) and groundnuts (2,035 ha, 10.5%). Together, these three crops account for over one-third of Tonga’s total agricultural land use.
- Production volume: Coconuts were the top crop with 68,758 tones, followed by pumpkins, squash, and gourds (20,654 t), and cassava (7,123 t).
Note 1: Due to differences in data sources, definitions, and calculation methods, figures for Agricultural Value Added and Gross Agricultural Production Value may vary. Value Added typically reflects net output after intermediate inputs, while Gross Production refers to the total market value of agricultural output before deductions. - Note 2: The Gross Production Value of Agricultural Production correspond to 2002, while the harvested area (19,345 hectares “ha”) and production (131,314 tones “t”) correspond to 2023. - Source: World Bank - FAOSTAT
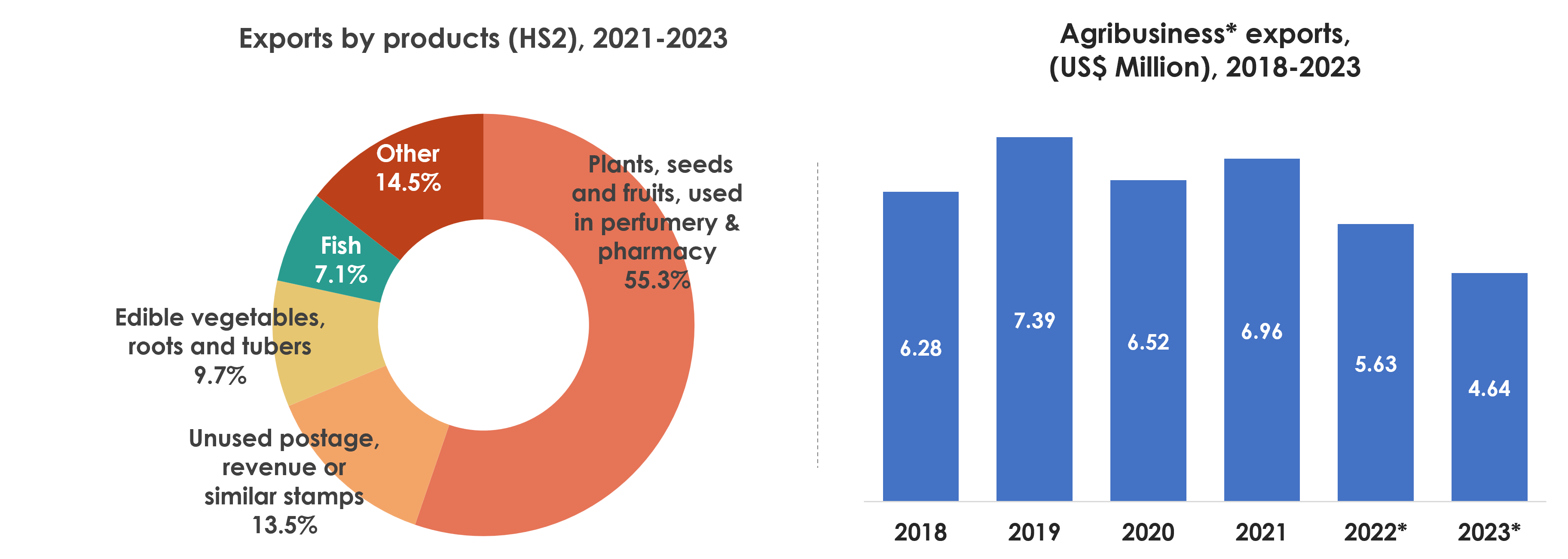
- Backbone of trade and exports: Over the past three years, agriculture has accounted for an average of 70% of Tonga’s total exports, highlighting its critical role in the national economy and foreign exchange earnings.
- Declining but dominant: While agribusiness exports fell from US$7.39 million in 2019 to US$4.64 million in 2023, the sector still constitutes the majority of Tonga’s export economy.
* Excludes live animals and edible animal products. - Source: TradeMap.com - FAOSTAT
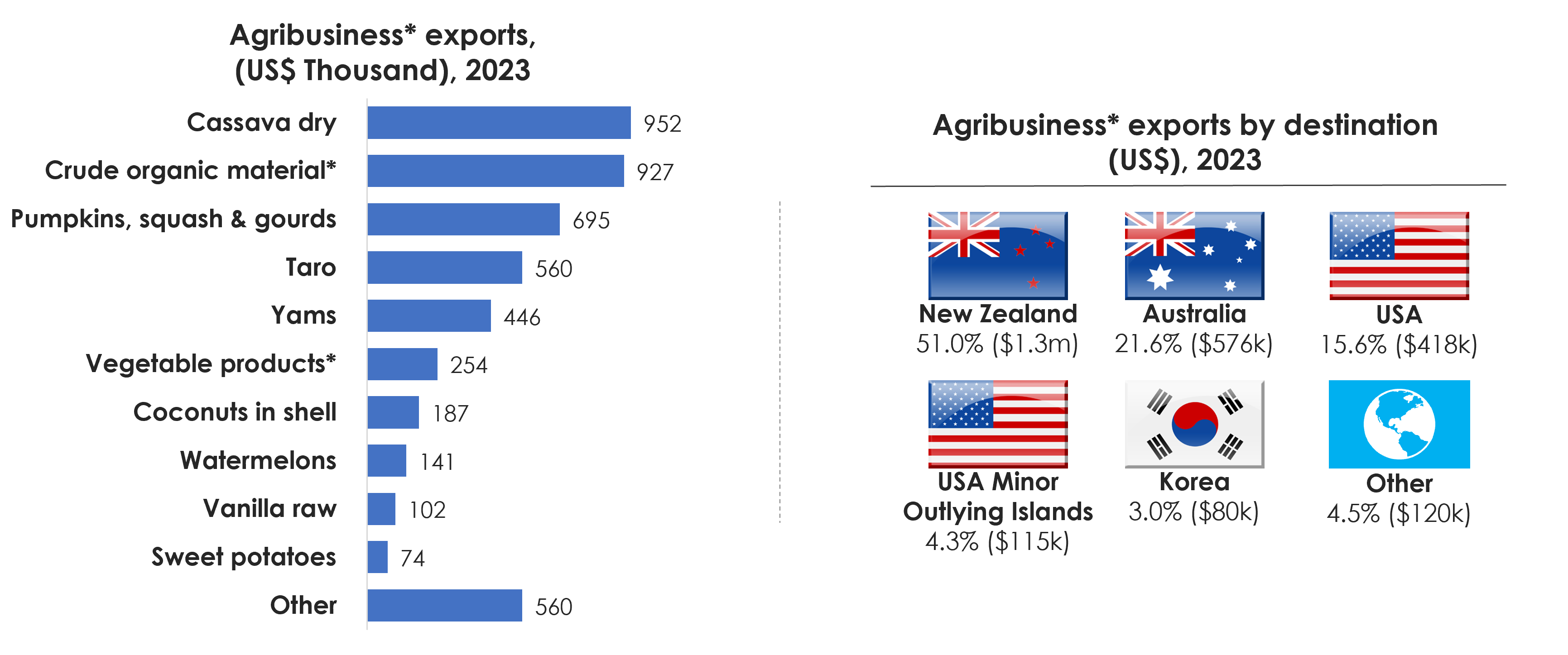
- Top agribusiness exports: In 2023, Tonga's leading agribusiness export was dry cassava (US$952k), followed by pumpkins, squash & gourds (US$695k) and taro (US$560k). These top three products represent a strong foundation for agro-processing and export diversification.
- Export destinations dominated by regional partners: New Zealand leads as the top export market, receiving 51% of Tonga’s agribusiness exports (US$1.3 million), followed by Australia (22%, US$576k) and the USA (16%, US$418k). Together, these three countries account for over 85% of the flows.
* Not elsewhere classified (n.e.c.) - Note: The total sum of values may differ between charts due to the use of different data sources. - Source: FAOSTAT - TradeMap.com
